H-1B Visa:
A Complete Guide
to Securing U.S. Jobs.
H-1B visa allows U.S. companies to hire foreign workers in specialized fields, such as technology and healthcare.
H-1B visa is capped at 85,000 new visas per year. This competitive visa allows skilled foreign workers in specialty fields to stay in the U.S. for up to six years.
Work in the U.S.
Gain employment in specialized
fields at leading companies.
Dual Intent
Apply for a Green Card,
while maintaining your H-1B visa.
Family Inclusion
Bring your spouse and children
under the H-4 visa.
Competitive Salary
Benefit from prevailing wage
requirements ensuring fair pay.
Career Flexibility
Transfer to a new employer without
needing to re-enter the lottery.
Client
Satisfaction
Years
in the business
H-1B Visa
Overview and Key Benefits
The H-1B visa is one of the most sought-after non-immigrant visas in the U.S. It allows companies to hire foreign professionals in specialized occupations that require at least a bachelor’s degree or equivalent experience. Whether you are an employer looking to hire global talent or a foreign worker pursuing professional opportunities, understanding the H-1B visa’s eligibility and benefits is essential.
What is the H-1B Visa?
Foreign workers in fields such as IT, engineering, healthcare, and more may qualify for an H-1B visa, but both the employer and the foreign worker must meet specific eligibility criteria. The job position must be classified as a "specialty occupation," meaning it requires specialized knowledge and at least a bachelor's degree. The foreign worker must hold at least a U.S. bachelor’s degree or its equivalent from another country in the relevant field. Additionally, the U.S. employer must sponsor the visa by filing a petition on behalf of the worker, demonstrating the need for their expertise.
Top Benefits of the H-1B Visa for Foreign Workers
Foreign workers pursuing the H-1B visa enjoy several benefits, making it one of the most attractive employment visa categories. Here’s why:
- Work Authorization: The H-1B visa allows foreign professionals to work in the U.S. for up to three years, with the option to extend up to six years.
Path to Permanent Residency: H-1B visa holders can apply for a Green Card and transition to permanent residency status.
- Dependent Visa Options: H-1B visa holders can bring their immediate family (spouse and children) through the H-4 visa, with some dependents eligible for work authorization.
H-1B Visa Success Rate.
The success rate for H-1B visas varies based on factors such as the annual cap, employer filings, and the applicant’s qualifications. the overall selection rate for the lottery can be much lower, especially given that demand often exceeds the available 85,000 H-1B visa slots.
00%
Depending on the
each year's demand
H1B Visa Application Costs and Processing Timeline
An overview of fees and processing times for applying to the H1B Visa program, which allows U.S. employers to hire foreign professionals.
Application Fees
- Form I-129 Filing Fee: $460
- ACWIA Fee: $750 - $1,500
- Public Law 114-113 Fee: $4,000
- Fraud Prevention and Detection Fee: $500, for new H1B petitions.
- Premium Processing Fee: $2,500
Application Timeline
- Standard Processing Time: 3 to 6 months
- Expedited Processing: 15 days with a premium processing
FAQs
About H-1B Visa.
What are the chances of getting selected in the H-1B lottery?
The H-1B visa is subject to an annual cap of 85,000 visas (65,000 for regular applicants and 20,000 for those with advanced degrees from U.S. institutions). Given the demand, the chances of selection in the lottery can vary, with an estimated selection rate of 20-30% based on recent years.
Can more than one company file an H-1B petition for me?
Yes, multiple companies can file H-1B petitions for the same individual, but a single company cannot submit more than one petition. Submitting multiple petitions increases the chances of being selected in the lottery, though USCIS has implemented stricter rules to prevent abuse.
How can I transfer my H-1B visa to another employer?
You can transfer your H-1B visa to a new employer by having them file a transfer petition, Form I-129, with USCIS. The process does not require going through the lottery again, and you can start working for the new employer as soon as USCIS receives the transfer petition.
Can H-1B visa holders bring their spouse and children to the United States?
Yes, H-1B visa holders can bring their spouse and children (under 21) to the U.S. on H-4 visas. H-4 visa holders can live and study in the U.S., and spouses may apply for employment authorization under certain conditions.
What are the wage requirements for H-1B sponsorship?
Employers must pay H-1B workers at least the prevailing wage for the role, as determined by the U.S. Department of Labor. This ensures that the hiring of foreign workers does not undercut U.S. labor market conditions
Clients we
work for.
















H-1B Visa Lottery and Selection Process
H-1B visa process is highly competitive, especially due to the annual cap imposed by the U.S. government. Understanding how the lottery system works and the chances of being selected is crucial for both employers and applicants.
A comprehensive Guide to how Does the H-1B Lottery Work?
The U.S. government sets an annual limit of 65,000 H-1B visas for foreign workers with a bachelor’s degree and an additional 20,000 for those holding a master’s degree from a U.S. institution.
Key Steps in the H-1B Lottery Process:
- Registration: Employers must register their prospective employees for the lottery during a specific window in March.
- Lottery Rounds: There are two lottery rounds. The first round selects 65,000 applicants, while the second lottery picks from those with advanced degrees.
- Selection and Petition Filing: If selected, employers have 90 days to file an H-1B petition with USCIS.
Understanding the Advanced Degree Cap in the H-1B Lottery
There are two categories in the lottery system:
- Regular Cap: 65,000 visas are awarded to individuals holding at least a bachelor’s degree.
Advanced Degree Cap: An additional 20,000 visas are reserved for those with a U.S. master’s degree or higher. Advanced degree applicants are first entered into the advanced degree lottery; if not selected, they automatically get another chance in the regular lottery.
Statistical Trends in H-1B Lottery Results
In recent years, the H-1B visa program has seen a significant increase in demand. For instance, in fiscal year (FY) 2023, the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) received over 483,000 H-1B petitions—a sharp rise from around 275,000 petitions in FY 2022. Despite the high demand, only 85,000 visas are issued annually, including 65,000 for general applicants and an additional 20,000 reserved for individuals with advanced degrees from U.S. institutions.
Approval rates have fluctuated over time. Between 2017 and 2020, under stricter immigration policies, the denial rate for initial H-1B petitions peaked at 15%, compared to an average of 6-7% in earlier years. In FY 2021, the denial rate dropped to 4%, following changes in immigration policy under the Biden administration.
H-1B Lottery, Dates and Deadlines
Each year, the lottery follows a strict timeline:
- Registration Period: Opens in early March.
- Lottery Results: Announced in late March or early April.
- Petition Filing: Employers must file the H-1B petition by June 30 for selected candidates.
Keeping track of these dates ensures a smooth application process for both employers and applicants.
Eligibility Requirements for the H-1B Visa
To be eligible for an H-1B visa, the applicant must have a job offer in a specialty occupation that requires specialized knowledge and at least a bachelor’s degree or its equivalent in a related field. Additionally, the U.S. employer must sponsor the applicant by filing a petition with USCIS on their behalf.
Who Can Apply for the H-1B Visa?
To qualify for an H-1B visa:
- Job Requirements: The position must require specialized knowledge, with at least a bachelor’s degree in a related field.
- Applicant Requirements: Applicants must hold the required degree and show professional expertise.
- Employer Requirements: The U.S. employer must file the H-1B petition and prove they can offer the wage levels and working conditions stipulated in the job description.
What is a Specialty Occupation in the H-1B Visa?
A specialty occupation refers to a job that requires:
- Theoretical and practical application of specialized knowledge.
- At least a bachelor’s degree or higher in the relevant field.
- Expertise in areas such as IT, engineering, architecture, healthcare, finance, or scientific research.
- A role that is complex or unique, requiring advanced skills and education.
- Specialized training and experience that are not easily attainable without a formal academic background.
Employer Sponsorship: Key Requirements for H-1B Visa
- File a Labor Condition Application (LCA) with the Department of Labor (DOL).
- Offer wages that meet or exceed the prevailing wage for the position.
- Provide documentation proving the applicant meets all job requirements.
Understanding the Labor Condition Application (LCA) for H-1B Visa
The Labor Condition Application (LCA) is a document that:
- Certifies that the employer will pay the foreign worker a wage equal to or greater than the prevailing wage for the job.
- Ensures that hiring the foreign worker won’t negatively impact the working conditions of U.S. workers in similar positions.
H-1B Visa Application Process: Filing and Fees
Applying for the H-1B visa is a multi-step process that involves careful preparation and adherence to deadlines. From filing fees to essential documents, here’s a comprehensive guide on what you need to know as an employer or employee applying for an H-1B visa.
How to File an H-1B Petition: Employer’s Guide
Employers play a central role in the H-1B visa process as they are the ones petitioning for their foreign worker’s visa. The process involves several key steps:
Determine Eligibility:
Ensure that the job position qualifies as a specialty occupation and that the applicant meets the educational and professional requirements.
File a Labor Condition Application (LCA):
Submit the LCA to the Department of Labor, affirming that the foreign worker will be paid the prevailing wage and that hiring will not adversely affect U.S. workers.
File Form I-129 (Petition for a Nonimmigrant Worker):
Once the LCA is certified, the employer files Form I-129 with the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
Submit Supporting Documents:
Along with Form I-129, include documentation proving the applicant’s qualifications and the employer’s ability to pay the wage.
H-1B Filing Fees: Complete Cost Breakdown
Filing for an H-1B visa involves multiple fees that must be covered by the employer. Employers are responsible for most of the fees, but some, like the premium processing fee, may be paid by the employee. Here is a breakdown of the costs:
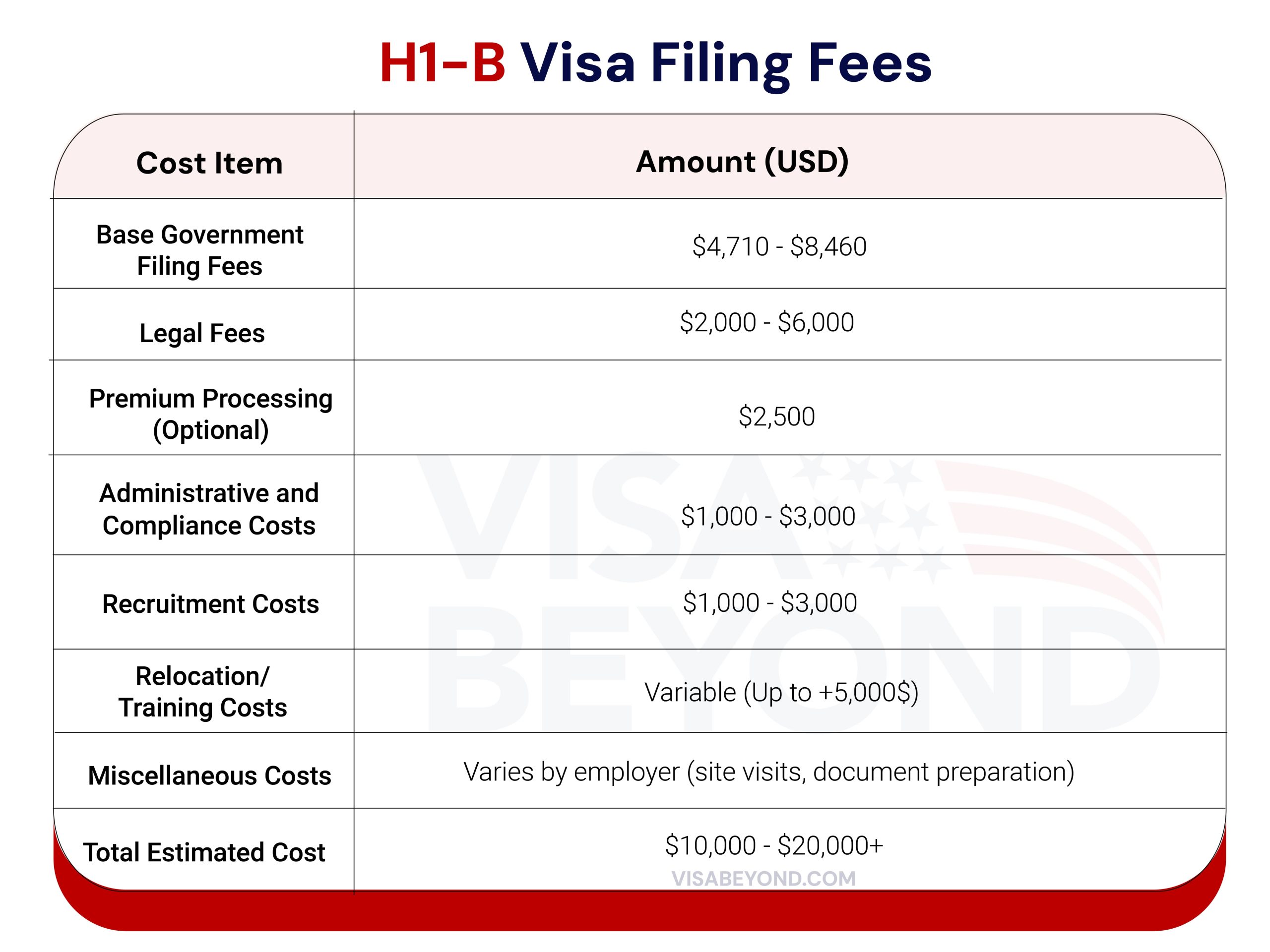
Essential Documents Required for H-1B Visa Filing
Both the employer and the employee must provide specific documents during the H-1B petition process. Below is a list of essential documentation:
- From the Employer:
- Certified Labor Condition Application (LCA) from the Department of Labor.
- Form I-129: Completed Petition for Nonimmigrant Worker.
- Proof of business operations, such as tax returns or company registration documents.
- From the Employee:
- Copy of passport (valid for at least six months beyond the intended stay).
- Copies of degree certificates and transcripts.
- Proof of work experience or professional qualifications (e.g., letters from previous employers).
- Offer letter from the sponsoring employer.
Tips for Completing Form I-129:
- Double-check all information for accuracy, particularly spelling of names and passport details.
- Include all required supporting documents when submitting the form to USCIS.
- Use premium processing if you need a faster decision (within 15 calendar days).
H-1B Visa Processing and Timelines
The H-1B visa process can take several months, depending on factors like lottery selection and whether premium processing is used. It’s essential to be aware of the general timeline for processing.
H-1B Visa Processing: What to Expect
H-1B visa processing timeline varies depending on the type of processing selected. Regular processing can take anywhere from 3 to 6 months, while premium processing, which costs an additional fee, expedites the review to 15 calendar days. The timeline also depends on factors like the complexity of the case and the USCIS workload, with some applicants experiencing delays during the lottery or petition review stages.
Here’s a breakdown of the typical H-1B visa processing timeline from start to finish:
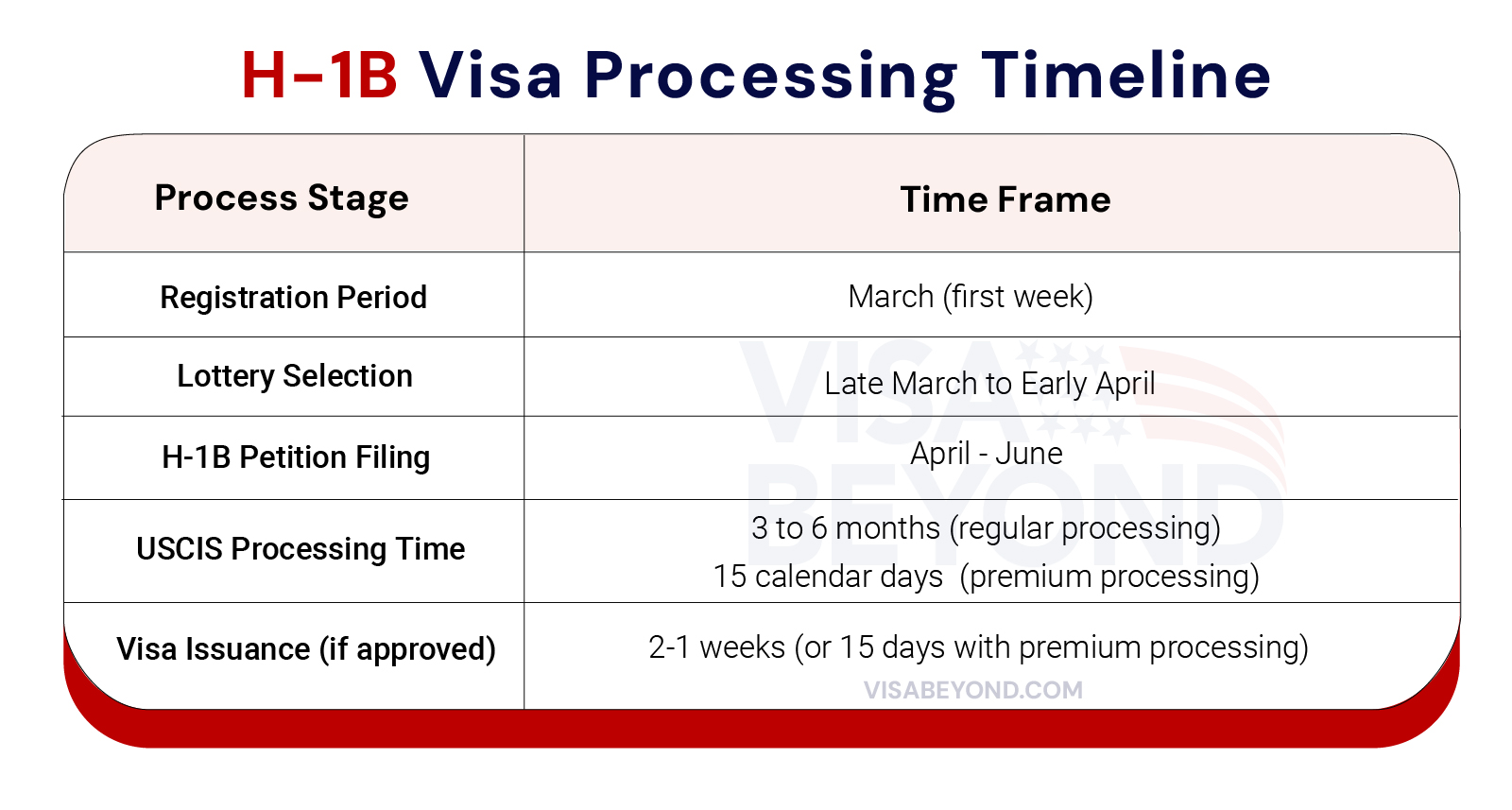
Keep in mind that even after approval, the visa is typically issued 10 days before the start of employment, which is usually on October 1 of the fiscal year.
Expedited H-1B Processing: Is Premium Processing Worth It?
Premium processing allows for a decision on your H-1B petition within 15 calendar days for a fee of $2,500. Here are the pros and cons of opting for premium processing:
- Pros:
- Faster Processing: A decision is guaranteed within 15 days.
- Ideal for Time-Sensitive Cases: If an employee needs to start work quickly, premium processing is the best option.
- Cons:
- Additional Cost: The $2,500 fee can be expensive for employers.
- No Guarantee of Approval: Premium processing only speeds up the decision; it does not guarantee approval.
H-1B Visa Transfer: Changing Employers
If you’re already on an H-1B visa and want to change employers, the H-1B transfer process allows you to work for a new company without losing your visa status.
How to Transfer Your H-1B Visa to a New Employer
Job Offer:
The worker must first receive a job offer from a new employer.
File a New Petition:
- The new employer must file a Form I-129 and follow the same process as a new H-1B visa petition, but without the lottery.
Start Work Immediately:
Once USCIS receives the new petition, the employee can start working for the new employer even before the petition is approved.
The O-1 visa is initially granted for up to three years, with the possibility of extensions. Understanding the validity period, how to apply for extensions, and the renewal process is crucial for maintaining your status and continuing your work in the U.S.
Legal Considerations When Changing Employers on H-1B Visa
Here are some key legal considerations to keep in mind during the H-1B transfer process:
- No Cap Restriction: Since you are already on an H-1B visa, you are not subject to the H-1B lottery cap again.
H-1B Portability: You can begin working with your new employer as soon as USCIS receives the transfer petition, but if the petition is denied, you must stop working immediately.
Impact of H-1B Transfer on H-4 Dependents
If you have family members on H-4 dependent visas, their status will remain the same after an H-1B transfer. However, the new employer must file for an H-4 extension along with the H-1B transfer to keep their status valid.
This content is informative, well-structured, and optimized for search engines, ensuring a balance between engaging style and detailed information that potential applicants would be seeking. The charts, tables, and lists provide clarity on key steps, costs, and timelines while maintaining reader engagement.
H-1B Visa Extensions: How to Extend Beyond Six Years
While the initial H-1B visa is granted for up to three years, it can be extended for an additional three years, allowing a total of six years of employment in the U.S. However, what happens when your six years are up? Fortunately, there are options to extend beyond this limit, especially if you’re pursuing a Green Card or under certain exceptional circumstances.
How to Extend Your H-1B Visa: Key Steps
If you’re nearing the end of your six-year H-1B stay, here are the key steps you and your employer can take to extend your H-1B visa:
- Ensure Eligibility: Extensions beyond six years are typically only available if your Green Card process has been initiated or if you’re eligible under certain exemptions, such as time spent outside the U.S. while on H-1B.
- File Form I-129: To extend your stay, your employer must file another Form I-129 (Petition for a Nonimmigrant Worker) with U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
- Labor Condition Application (LCA): Just like the initial application, the employer must file a new LCA with the Department of Labor certifying that working conditions and wages will remain compliant.
- Wait for Approval: USCIS will process the extension petition, and you will be notified whether it has been approved or if additional evidence is required.
H-1B Extensions for Green Card Applicants
If your employer has started the process of sponsoring you for a Green Card, you may be eligible for additional H-1B extensions beyond the typical six years. Here’s how it works:
- AC21 Law: Under the American Competitiveness in the 21st Century Act (AC21), H-1B visa holders who have filed their I-140 (Immigrant Petition for Alien Worker) or PERM Labor Certification at least 365 days before their six-year limit can extend their H-1B status in one-year increments until they receive a decision on their Green Card application.
- Extensions for Approved I-140: If your I-140 petition is approved but your Green Card application is still pending due to visa backlogs, you can extend your H-1B status in three-year increments.
Let’s Make Your U.S. Dreams a Reality.
Handling H-1B Visa Denials , RFEs, and Appeals
Unfortunately, not all H-1B visa applications are approved the first time. If you receive a Request for Evidence (RFE) or your visa is denied, there are ways to address the issues and appeal decisions.
Top Reasons for H-1B Visa Denials and How to Avoid Them
Several factors can lead to an H-1B visa denial. Here are the most common reasons and how to avoid them:
Specialty Occupation Issues:
If USCIS believes the job doesn’t qualify as a specialty occupation, your application may be denied. To avoid this, provide detailed job descriptions and ensure the position requires specialized knowledge and a bachelor's degree or higher.
Insufficient Evidence:
Applications may be denied due to lack of supporting evidence, such as missing educational qualifications or job offers. Make sure all required documents are provided, including proof of the employee's qualifications and the employer’s ability to pay the salary.
Wage-Level Issues:
Applications can also be denied if the wage offered to the employee does not meet the prevailing wage for the position. Ensure that your LCA complies with wage regulations.
How to Respond to H-1B Request for Evidence (RFE)
Receiving an RFE is not a denial, but it means that USCIS needs more information to approve your petition. Here’s how to respond effectively:
- Review the RFE Carefully: Understand the specific issues USCIS wants more information on. Common RFEs focus on specialty occupation requirements, wage levels, or qualifications.
- Provide Comprehensive Evidence: Include detailed and well-organized documentation. For example, if the RFE questions the job’s specialty occupation, provide expert letters, detailed job duties, and industry standardsshowing that the job requires a specialized degree.
- Submit Within the Deadline: RFEs must be responded to within the specified timeline (usually 90 days). Late responses may result in denial.
Appealing an H-1B Visa Denial: What to Do
If your H-1B visa is denied, you have the option to file an appeal or a motion to reopen the case. Here’s how to proceed:
- Filing an Appeal: You can appeal the decision with the Administrative Appeals Office (AAO) if you believe the denial was incorrect. This is a formal process where you submit evidence and legal arguments against the denial.
- Motion to Reopen or Reconsider: Instead of appealing, you can file a motion to reopen if you have new evidence that wasn’t available during the initial petition, or a motion to reconsider if you believe USCIS made an error in applying the law.
- Consult an Attorney: It’s often wise to consult an immigration attorney to determine whether an appeal or motion is the best course of action based on your case.
Visa Alternatives After H-1B Denial
If your H-1B petition is denied, there are several alternative visa options to consider:
- O-1 Visa: If you possess extraordinary ability in your field, you may qualify for an O-1 visa. This visa is for individuals with proven excellence in fields like science, education, business, or the arts.
- L-1 Visa: If you work for a multinational company, you might qualify for an L-1 visa to transfer to a U.S. branch, subsidiary, or affiliate.
- TN Visa: If you are from Canada or Mexico, the TN visa under NAFTA might be an option for certain professional occupations.
Pathway from H-1B Visa to Green Card
Many H-1B visa holders aim to transition from temporary work status to permanent residency (Green Card). This section outlines the key steps involved in moving from an H-1B visa to a Green Card.
How H-1B Visa Holders Can Transition to a Green Card
To transition from H-1B status to a Green Card, follow these steps:
- PERM Labor Certification: Your employer must first file a PERM Labor Certification to demonstrate that no qualified U.S. workers are available for the job. This is the first step toward an employment-based Green Card.
- File Form I-140: Once the PERM certification is approved, your employer must file Form I-140 (Immigrant Petition for Alien Worker) with USCIS.
- Wait for Priority Date: Depending on your home country, there may be a waiting period before your Green Card application can proceed.
- File Form I-485 (Adjustment of Status): Once your priority date becomes current, you can file Form I-485 to adjust your status to permanent residency.
Understanding the PERM Labor Certification for H-1B Visa Holders
The PERM Labor Certification is a crucial step in the Green Card process. It proves that there are no qualified U.S. workers available for the job. Here’s what’s involved:
- Recruitment Process: The employer must conduct a recruitment process to show that they attempted to hire U.S. workers for the position.
- Department of Labor Approval: Once the recruitment process is complete, the employer submits the PERM application to the Department of Labor for certification.
- Timeline: The PERM process can take several months, so it’s important to start early.
Concurrent Filing of I-140 and I-485 for Green Card
In some cases, you can file both Form I-140 and Form I-485 at the same time. This is called concurrent filing and offers several advantages:
- Faster Processing: Concurrent filing can speed up the Green Card process, especially for countries without long wait times.
- Work Authorization: You can apply for Employment Authorization (EAD) and Advance Parole to work and travel while your Green Card is being processed.
Maintaining H-1B Status While Applying for a Green Card
While waiting for your Green Card to be processed, it’s crucial to maintain your H-1B status to avoid falling out of legal status. To ensure this, make sure to file timely H-1B extensions, especially if your I-140 or PERM certification is still pending. Once your Form I-485 is filed, you can apply for Employment Authorization (EAD), allowing you to work without needing further H-1B extensions. Be sure to avoid any gaps by ensuring that either your H-1B status or EAD remains valid until your Green Card is approved.
How to Find H-1B Sponsorship and Top Employers
Securing an H-1B visa sponsorship is a critical step for foreign workers looking to work in the U.S. Since the process can be competitive, it’s important to know where to focus your efforts and which industries and companies are most likely to sponsor H-1B visas.
Finding H-1B Sponsorship: Key Tips and Resources
Finding an H-1B sponsor can be a challenging process, but following these tips can help you increase your chances of success:
Research Companies That Have Sponsored H-1B Visas Before:
Use resources like the USCIS H-1B Employer Data Hub or other websites to identify companies with a history of sponsoring H-1B visas.
Target Industries with High Demand:
Some industries, like technology, healthcare, and engineering, are more likely to sponsor H-1B visas due to their need for specialized talent.
Networking:
Build connections through platforms like LinkedIn or by attending career fairs that attract multinational companies with a high likelihood of sponsorship.
Top U.S. Companies Sponsoring H-1B Visas
Certain companies are known for consistently sponsoring H-1B visas, particularly in fields like tech, finance, and healthcare. Here are some of the top U.S. companies that sponsor H-1B visas:
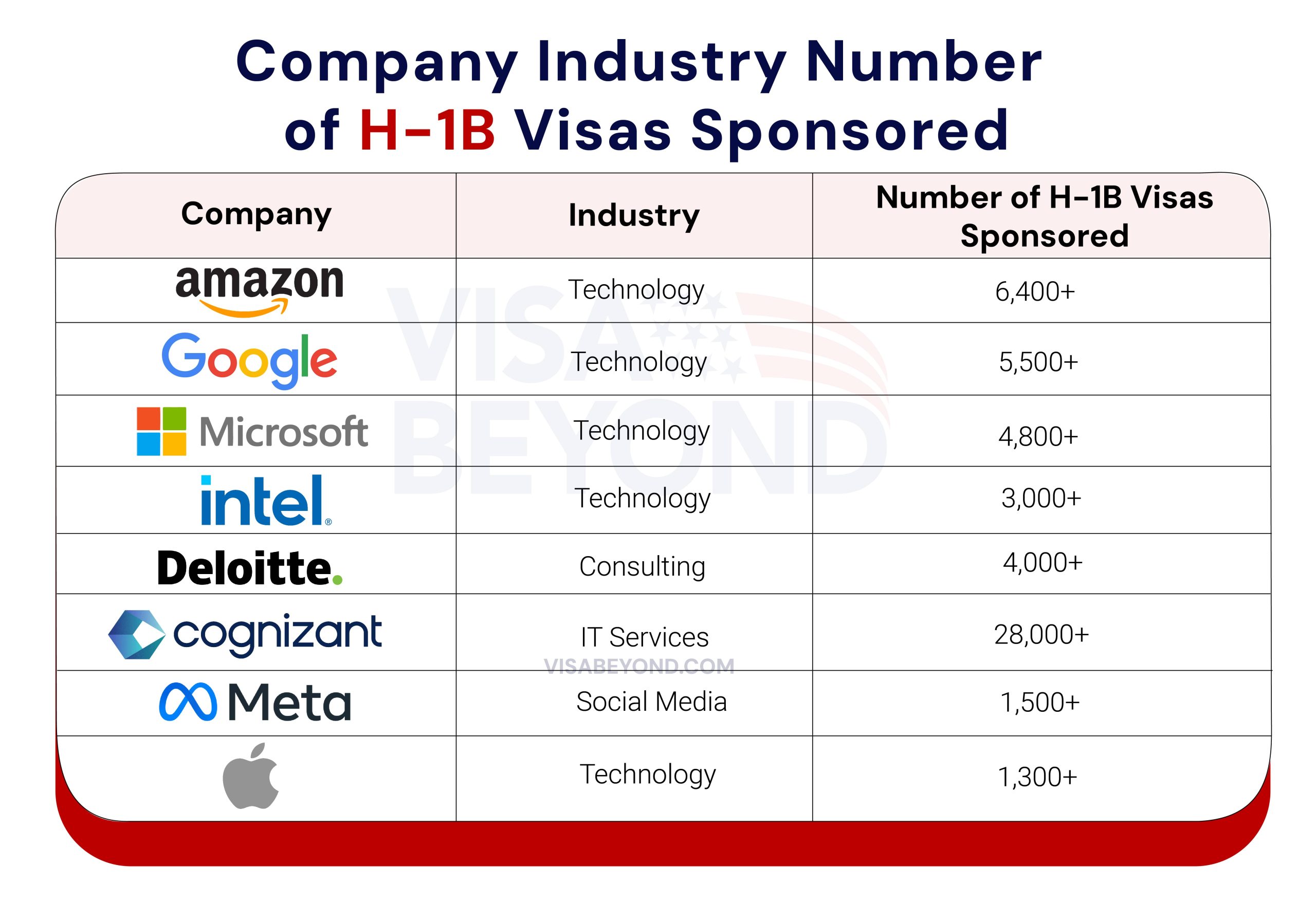
These companies have a proven track record of sponsoring H-1B workers and are often actively hiring talent from abroad.
Industries with the Highest Demand for H-1B Visa Holders
Certain industries consistently show higher demand for H-1B visa holders due to their need for specialized skills. Below is a breakdown of the top industries hiring H-1B workers:
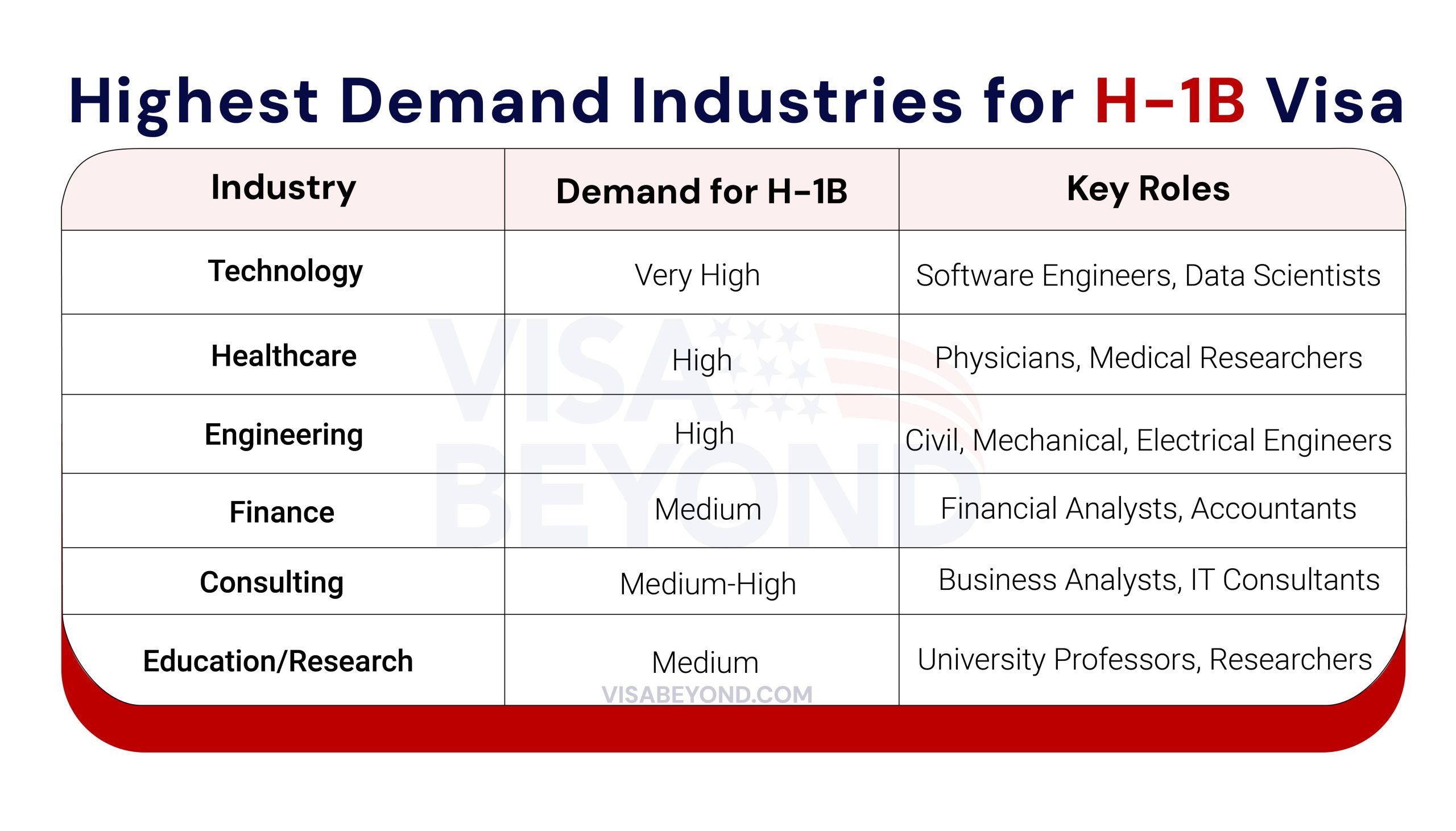
Legal and Compliance Requirements for H-1B Employers
H-1B employers must comply with a range of legal and regulatory requirements to hire foreign workers. Understanding these responsibilities is essential for both the employer and the H-1B visa holder to ensure compliance with U.S. laws.
Labor Condition Application (LCA): Employer Obligations
Before an employer can file for an H-1B visa, they must first submit a Labor Condition Application (LCA) to the Department of Labor (DOL). The LCA is designed to ensure that the employment of the foreign worker will not negatively impact U.S. workers. Here’s what the employer must commit to:
- Wages: The employer must agree to pay the H-1B worker at least the prevailing wage for the position.
- Working Conditions: The employer must ensure that the working conditions for H-1B employees are comparable to those of U.S. workers.
- No Labor Disruption: The LCA requires the employer to confirm that hiring the H-1B worker will not adversely affect the working conditions of other employees.
Wage and Job Title Requirements for H-1B Sponsorship
Employers must meet specific wage and job title requirements when sponsoring H-1B workers:
- Prevailing Wage: The wage offered must meet or exceed the Department of Labor’s calculated prevailing wage for the job in the region.
- Job Title Compliance: The job title must accurately reflect the role and responsibilities of the employee and must require specialized knowledge and a minimum of a bachelor’s degree.
Posting LCA Notice and Other Employer Compliance Steps
Once the LCA is filed, the employer is required to post notices in two conspicuous locations at the workplace or electronically to inform employees of the H-1B sponsorship:
- Posting Notice: The LCA must be posted 10 days before filing the H-1B petition. This informs current employees about the hiring of the foreign worker.
- Public Access File: Employers must maintain a public access file with relevant LCA documentation that can be reviewed by government officials or U.S. workers upon request.
How to Handle Site Visits and Audits for H-1B Employers
Employers who sponsor H-1B workers may be subject to site visits and audits from the Department of Labor (DOL) or USCIS to ensure compliance with H-1B regulations. Here’s how to prepare:
- Be Ready for Unannounced Visits: Site visits are usually unannounced. Employers should have all documentation related to the H-1B worker, including the LCA, wage records, and job description.
- Cooperate with Inspectors: During the visit, employers must provide inspectors access to relevant documents and allow them to interview the H-1B worker if necessary.
- Ensure Record-Keeping: Proper record-keeping is essential for a smooth audit. Keep all employment records up to date and in compliance with the H-1B regulations.
Maximizing Your H-1B Visa Experience
Being on an H-1B visa offers numerous career opportunities. However, maximizing these opportunities requires strategic planning and a focus on long-term goals. Here’s how to make the most of your time as an H-1B worker.
Strategizing Career Growth on an H-1B Visa
To grow your career while on an H-1B visa, focus on building skills and positioning yourself for long-term opportunities, both within your company and beyond:
- Pursue Advanced Certifications: Employers value workers who continue to improve their skills. Earning certifications in areas like project management or specialized software can boost your profile.
- Seek Leadership Roles: Don’t hesitate to take on more responsibilities. Ask for leadership opportunities within your team to build your management skills.
- Plan for Permanent Residency: Start the process for a Green Card as early as possible to secure your long-term future in the U.S.
Resources and Support for H-1B Visa Holders
There are several resources available for H-1B workers to help them navigate the visa process, career development, and legal matters:
- USCIS: The official U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services website provides detailed information about the H-1B visa.
- Professional Networks: Join LinkedIn groups for H-1B visa holders to network and share experiences.
Building a Community of Support as an H-1B Worker
Building a community of support is essential for professional and personal growth during your time in the U.S.:
- Join Professional Associations: Many industries have professional associations that welcome H-1B workers. These organizations offer networking opportunities and access to industry events.
- Online Communities: Join online forums and social media groups focused on H-1B workers to share information, seek advice, and build connections with others in similar situations.
- Cultural Organizations: Many cities have local cultural or expat groups that help foreign workers adjust to life in the U.S. and build a network of support.
Final Thoughts: Successfully Navigating the H-1B Visa Process
The H-1B visa opens doors to incredible opportunities for skilled professionals to advance their careers and contribute to the thriving industries in the U.S. It not only allows you to bring your specialized expertise to one of the world’s largest economies but also provides a pathway to long-term growth and even permanent residency. With the right planning and determination, the H-1B visa can be your stepping stone to realizing your dreams and making a meaningful impact on your chosen field. The possibilities are vast, and the rewards are limitless!
Latest News.
From the blog

-
- Posted by Alvez

-
- Posted by Alvez
"*" indicates required fields


