M1 Visa Guide:
A Complete
Overview.
The M1 Visa is a non-immigrant visa for international students who want to pursue vocational or technical training in the U.S.
This Visa allows international students to enroll in U.S. vocational programs, such as technical, mechanical, or flight training, with a focus on non-academic education.
Hands-on Skills
Get specialized vocational
training in the U.S.
Quick Completion
Finish studies faster
than academic routes.
Work Experience
Gain 6 months
OPT post-training.
Family Together
Bring your spouse and
kids with M2 visas.
Career Growth
Transition to U.S. jobs
with H1B options.
Client
Satisfaction
Years
in the business
M1 Visa Overview
and Key Benefits
What is the M1 Visa? Eligibility and Key Benefits Explained
The M1 Visa is a non-immigrant visa for international students who wish to enroll in vocational or technical training programs in the U.S. Unlike the F1 Visa, which is for academic studies, the M1 Visa is specifically designed for students looking to acquire hands-on training in fields such as aviation, culinary arts, technical schools, and trade institutions.
Key Benefits of the M1 Visa
- Hands-on training in vocational and technical fields
- Access to accredited U.S. institutions offering specialized skills
- Eligibility for practical training after the program (OPT)
- Shorter time commitments for vocational courses compared to academic degrees
- Opportunity to gain U.S. experience for global job opportunities
M1 Visa for Vocational Students: An Introduction
Vocational education in the U.S. offers international students the opportunity to learn industry-specific skills that directly apply to their career. Whether it's a certificate program for auto mechanics, culinary training, or technical aviation courses, the M1 Visa helps students access the best institutions across these fields.
Examples of Vocational Programs
- Culinary Arts Schools: Learn from world-renowned chefs.
- Technical Schools: Specialize in fields like automotive repair or computer programming.
- Aviation Schools: Obtain professional pilot training with FAA-approved institutions.
M1 Visa Success Rate.
The success rate for Vocational Student Visa rate is similar to that of other student visas like the F1 Visa, provided that applicants meet all eligibility criteria, submit accurate documents, and demonstrate financial ability and intent to return home after studies.
However, this is not an official number and success can vary by country and individual circumstances. It’s crucial to meet all requirements for the best chance of approval.
00%
Depending on the
applicant’s country
M1 Visa Application Costs and Processing Timeline
An overview of fees and processing times for applying to the M1 Visa program for vocational and technical students.
Application Fees
- SEVIS I-901 Fee: $350
- DS-160 MRV Fee: $185
Application Timeline
- Processing Time: depending on the U.S. embassies location.
- Duration of Stay: duration of the study program
- Extensions possible
FAQs
About M1 Visa.
Can M1 Visa holders work in the U.S.?
M1 holders can only work on-campus and apply for up to 6 months of OPT after completing their program.
What is the difference between the M1 and F1 Visa?
M1 is for vocational training; F1 is for academic study. F1 offers more work flexibility (e.g., OPT, CPT).
How long can I stay in the U.S. on an M1 Visa?
M1 is valid for the length of the program plus a 30-day grace period, with a maximum stay of 3 years.
Can I extend my M1 Visa?
Yes, file Form I-539, but your total stay cannot exceed 3 years.
Can I bring my family on an M1 Visa?
Yes, spouses and children can join under M2 visas, but they face restrictions on work and study.
Can I transition from M1 to H1B or Green Card?
Yes, but you need an employer sponsor for an H1B or employment-based Green Card.
What happens if I overstay my M1 Visa?
Overstay can lead to a 3-10 year ban from the U.S. and impact future visa applications.
What programs are eligible for the M1 Visa?
Vocational programs like aviation, culinary arts, auto repair, and cosmetology are eligible.
Can I study part-time on an M1 Visa?
No, M1 requires full-time enrollment in a vocational program.
Clients we
work for.
















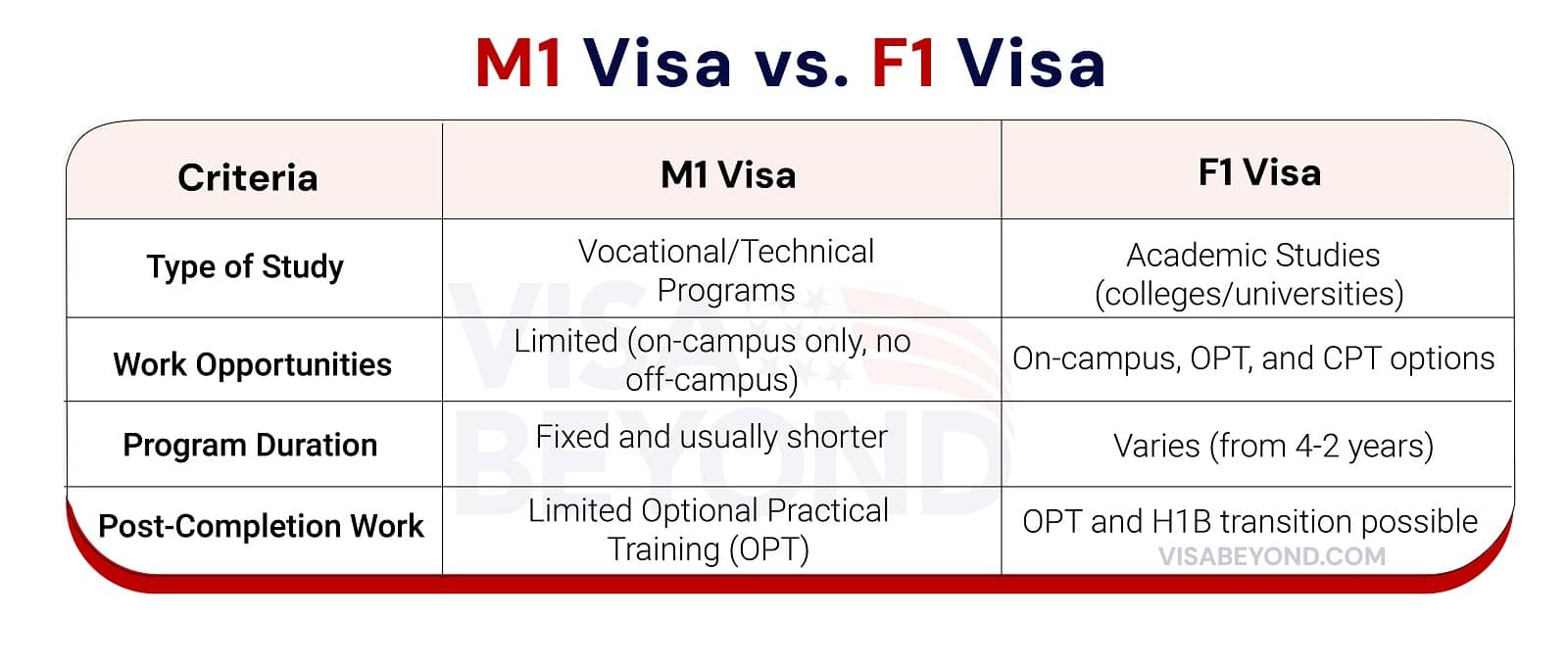
M1 Visa vs F1 Visa: What’s the Difference?
While both the M1 and F1 visas allow international students to study in the U.S., the type of education they focus on is quite different.
M1 Visa Eligibility and Requirements
Who is Eligible for the M1 Visa?
To qualify for the M1 Visa, applicants need to meet several specific criteria. These include:
- Enrollment in a vocational or technical program: Must be an accredited institution.
- Proof of financial support: Evidence that you can support yourself during your stay in the U.S.
- Non-immigrant intent: You must prove that you intend to return to your home country after completing your course.
Documents You Will Need:
- Valid passport
- Completed Form I-20 from your institution
- Proof of financial stability (bank statements, scholarships)
- SEVIS fee payment receipt
- Completed DS-160 form
Financial Support Requirements for M1 Visa
Unlike other visas, the M1 Visa requires strict proof of financial ability to cover both the tuition fees and living expenses for the entire duration of your study, as employment opportunities are limited.
Examples of Acceptable Financial Proof:
- Bank statements showing sufficient funds.
- Scholarship letters from a recognized sponsor.
- Affidavit of support if family members are funding your education.
Here’s a chart showing the minimum financial requirements for common vocational programs:

M1 Visa for Vocational and Technical Training Programs
Vocational and technical programs cover a wide range of fields, allowing students to gain hands-on experience and practical knowledge in their chosen industry.
Popular Programs Eligible for M1 Visa:
- Culinary Arts: Learn professional cooking techniques and restaurant management.
- Automotive Repair: Train to become a certified auto mechanic.
- Cosmetology: Obtain training in hair styling, makeup, and skin care.
- Aviation Maintenance: Gain the technical skills needed to repair and maintain aircraft.
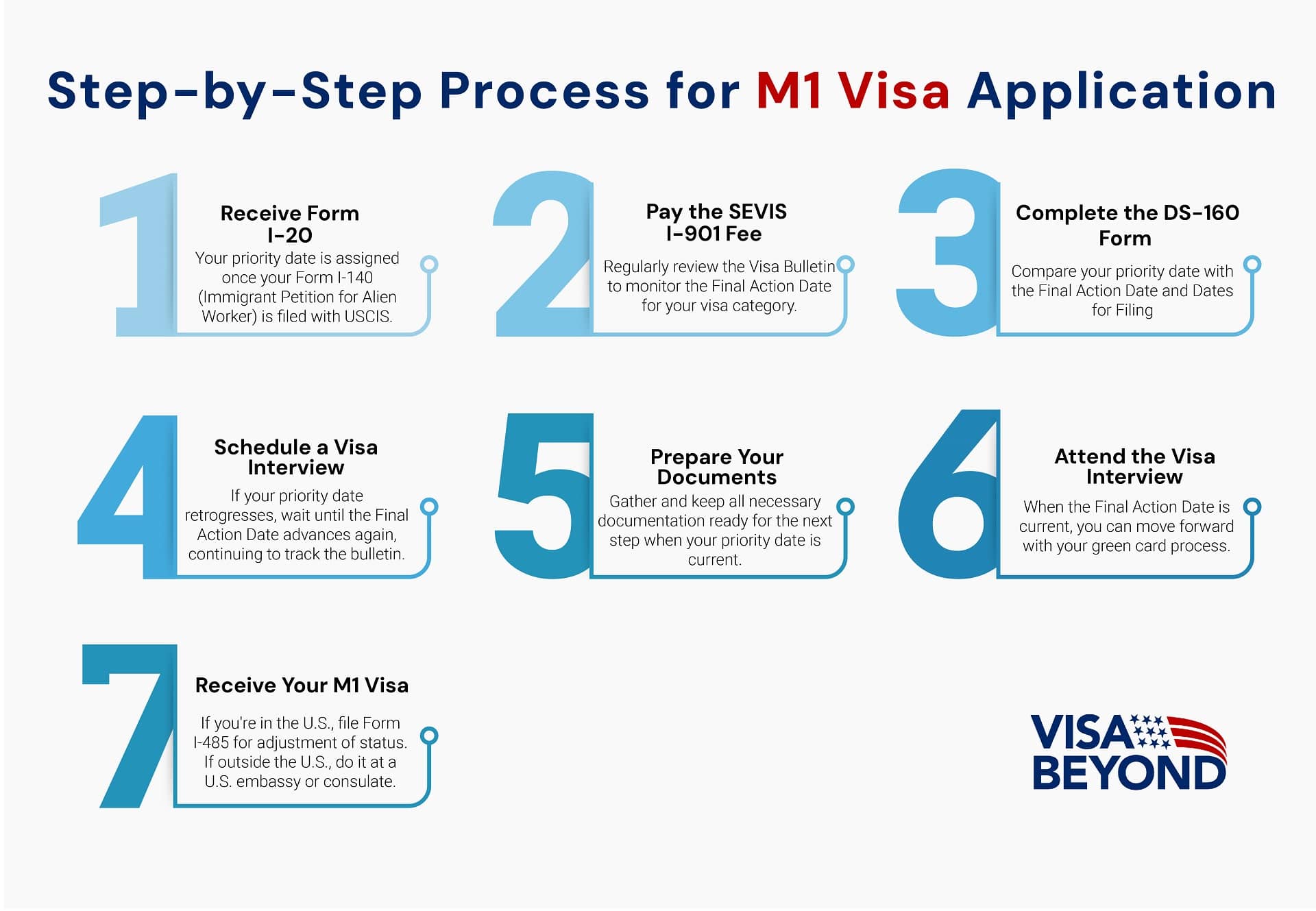
M1 Visa Application Process
How to Apply for an M1 Visa?
The process of applying for thisVisa is straightforward but requires careful attention to detail. Here’s a breakdown of the steps involved:
Visa Application Documents Checklist
Having the right documents ready is crucial for a successful M1 Visa application. Make sure to prepare the following:
- Passport (valid for at least 6 months beyond your intended stay)
- Form I-20 from your vocational school
- Completed DS-160 application
- SEVIS fee receipt
- Proof of financial support (bank statements, affidavits)
- Admission letter from the vocational school
Visa Interview: What to Expect and How to Prepare
The visa interview is often the most nerve-wracking part of the process. However, preparing for common questions can boost your chances of approval.
Common Questions Asked:
- Why did you choose this particular vocational program?
- How will you fund your education and stay in the U.S.?
- What are your plans after completing the program?
- Do you have any family or strong ties to your home country?
Tips for Success:
- Be honest and clear about your intentions.
- Bring all required documentation.
- Demonstrate that you plan to return to your home country after the program.
M1 Visa Work Restrictions and Opportunities
Can You Work on an M1 Visa?
The M1 Visa has strict restrictions on employment. M1 students are generally not allowed to work during their studies, except under very specific circumstances like on-campus jobs.
Employment Limitations:
- No off-campus work is permitted, unlike the F1 Visa.
- On-campus jobs are allowed but must be related to your field of study.
- Post-completion Optional Practical Training (OPT) is allowed, but only for a maximum of six months after completing your program.
Optional Practical Training (OPT) for M1 Visa Holders: Rules and Duration
M1 visa holders are eligible for Optional Practical Training (OPT) after completing their vocational program, but it comes with strict guidelines.
Key Rules:
- OPT is limited to 6 months, no extensions are permitted.
- OPT must be directly related to your field of vocational training.
- You must apply for OPT before the completion of your program.
Example: If you completed an aviation maintenance program, your OPT must be in a related job, such as working at an aircraft repair facility.
M1 Visa Duration, Extensions, and Maintenance
How Long is the M1 Visa Valid?
The M1 Visa is typically issued for the length of your vocational program plus a 30-day grace period. The total stay, including extensions, cannot exceed 3 years.
Example: If your program lasts 1 year, you will be granted an M1 Visa for that duration, plus an additional 30 days to prepare for your departure from the U.S.
How to Extend Your M1 Visa: Requirements and Process
You can apply for an M1 Visa extension if your program requires additional time for completion. However, you must show that the extension is justified, such as needing more time for practical training.
Steps for Extension:
- Submit Form I-539 to extend your stay.
- Provide documentation proving the need for additional time.
- Pay the associated fees and wait for approval.
Maintaining Your M1 Visa Status: Compliance and Regulations
To maintain your Visa status, you must comply with the following regulations:
- Maintain full-time enrollment in your vocational program.
- Report any address changes to your designated school official (DSO)
M1 Visa for Dependents
What is the M1 Visa ?
The M2 Visa allows the spouse and unmarried children under 21 of M1 visa holders to accompany them to the U.S. while they pursue vocational training. M2 visa holders can stay in the U.S. for the same duration as the primary M1 visa holder, with their visa expiring when the M1 visa holder’s stay ends.
Eligibility Requirements:
- Spouse: The legal spouse of the M1 visa holder.
- Children: Unmarried children under 21 years of age.
- Non-Immigrant Intent: Like the M1 visa, M2 applicants must prove they intend to return to their home country after the M1 visa holder’s studies are complete.
Can M2 Visa Holders Work or Study in the U.S.?
The M2 Visa has strict limitations on employment and education.
Work Limitations:
- M2 visa holders cannot work in the U.S. under any circumstances. They are ineligible for work authorization, making this visa primarily for dependents who wish to accompany the M1 holder.
Study Opportunities:
- Children of visa holders can attend K-12 schools, but spouses are not allowed to enroll in full-time educational programs.
- However, spouses can take recreational or part-time courses, like cooking classes or English as a Second Language (ESL) programs.
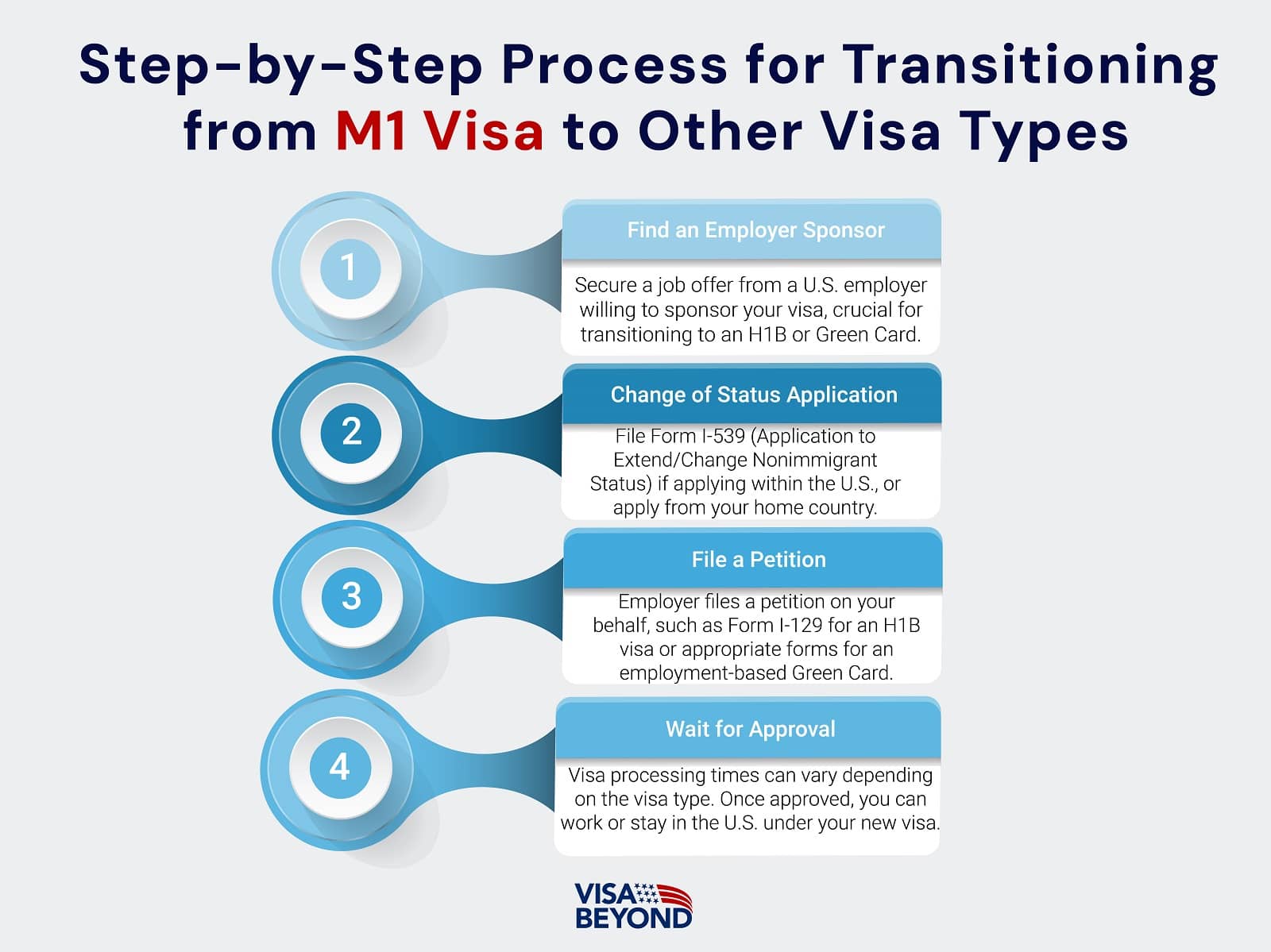
Transitioning from M1 Visa to Other Visa Types
Can You Transition from M1 Visa to H1B or Green Card?
Transitioning from an M1 Visa to an H1B or Green Card is possible but more complex compared to other visa types. M1 visa holders are typically expected to return to their home country upon completing their studies, but with strategic planning, a transition to employment-based visas like the H1B or even permanent residency (Green Card) can be achieved.
Key Options for Transition:
- H1B Visa: An M1 visa holder can switch to an H1B visa if they secure an employer willing to sponsor them for skilled work.
- Green Card: This route is less common but can be pursued if the M1 holder qualifies through employment-based categories, like EB-2 or EB-3, after completing their OPT.
Steps for Transitioning from M1 to Other Visa Types
Transitioning from M1 to another visa type requires careful navigation of the visa system.
M1 Visa Challenges and Solutions
Common Reasons for M1 Visa Denials and How to Avoid Them
While the M1 Visa is relatively straightforward, applicants may face denials for several common reasons.
Common Denial Reasons:
- Insufficient Financial Proof: Failure to show enough financial resources to cover tuition and living expenses.
- Lack of Ties to Home Country: If the consular officer believes you intend to stay in the U.S. permanently, your visa may be denied.
- Incomplete or Inaccurate Application: Missing documentation, incomplete forms, or inconsistencies in your application can lead to denial.
How to Avoid Denial:
- Provide clear financial evidence, such as bank statements or sponsorship letters.
- Demonstrate ties to your home country, like property ownership or family obligations.
- Double-check your application for errors and ensure all required documents are included.
What Happens If Your Visa Expires? Renewal and Overstay Rules
If your M1 Visa expires before you complete your studies or training, you must take action to avoid violating U.S. immigration laws.
Renewal Options:
- You can apply for an extension by filing Form I-539 if your course requires additional time. Extensions are granted on a case-by-case basis.
Consequences of Overstay:
- Unlawful Presence: Overstaying your visa can lead to penalties, including a ban on returning to the U.S. for 3 to 10 years.
- If you realize you are nearing the end of your stay, apply for an extension or prepare to leave the U.S. promptly to avoid overstay issues.
Maximizing Your M1 Visa Experience
How to Make the Most of Your M1 Visa Program
While on an M1 Visa, you have access to specialized training in your chosen field. Here’s how to maximize the opportunity:
Key Tips:
- Engage with your instructors: Build relationships with your teachers and mentors for future networking opportunities.
- Take advantage of OPT: Utilize the 6-month Optional Practical Training (OPT) period to gain real-world experience.
- Explore short-term certifications: Beyond your primary program, seek out short-term certifications or credentials that enhance your employability.
Networking and Building Professional Connections as an M1 Visa Holder
Building a professional network can significantly enhance your post-completion career opportunities, even if your visa limits employment options.
Networking Strategies:
- Attend industry events: Look for conferences, seminars, or networking events related to your field.
- Join student associations: Many vocational schools have clubs or groups that connect you with industry professionals.
- LinkedIn connections: Build a LinkedIn profile and connect with professionals in your industry for future job leads or recommendations.
Let’s Make Your U.S. Dreams a Reality.
M1 Visa to Employment
Navigating Employment Options After M1 Visa
After completing your vocational program, you have limited employment opportunities under the M1 Visa, but planning can help you transition to employment.
Employment Options After M1 Visa:
- Optional Practical Training (OPT): M1 visa holders are eligible for a maximum of 6 months of post-completion OPT, provided the job is directly related to their field of study.
- Transition to H1B: If you find an employer willing to sponsor you, you may be able to switch to an H1B visa for full-time employment.
Challenges of Transitioning from M1 Visa to Long-Term Employment
Moving from an M1 Visa to long-term employment presents unique challenges due to the visa’s restrictions.
Key Challenges:
- Limited OPT time: The 6-month OPT period is significantly shorter than the F1 Visa’s 12-month OPT.
- No automatic pathway to H1B: You must actively seek a job and sponsorship; there is no direct transition from M1 to H1B.
- Work Limitations: If you do not secure OPT or another visa in time, you will have to leave the U.S. upon completion of your program.
By understanding these challenges and planning accordingly, you can navigate the transition from Vocational Student Visa status to long-term employment or another visa type more smoothly.
M1 Visa Summary
This Vocational Student Visa is designed specifically for international students seeking to pursue vocational or technical training programs in the U.S. It offers opportunities for hands-on learning in fields such as culinary arts, aviation, automotive repair, and other specialized trades.
Key Points to Remember:
- Duration and Extensions: The M1 Visa is valid for the length of your program, plus a 30-day grace period, and extensions are limited to a total stay of 3 years.
- Work Limitations: Employment is restricted, with only on-campus work allowed and Optional Practical Training (OPT) available for up to 6 months post-completion.
- Dependents (M2 Visa): Spouses and children can accompany M1 holders but face restrictions on both work and full-time education.
- Transitioning to Other Visas: Transitioning from M1 to H1B or a Green Card is possible but requires employer sponsorship and careful planning.
- Compliance and Status Maintenance: Maintaining status by following program requirements and reporting any changes (address, program duration) is essential to avoid visa issues.
Overall, the Vocational Student Visa is ideal for students who aim to acquire specific vocational skills in a structured U.S. educational environment. However, careful planning is needed to navigate its limitations and maximize opportunities for work and further visa options.
Latest News.
From the blog

-
- Posted by Alvez

-
- Posted by Alvez
"*" indicates required fields


