U.S. Immigration Business Plans for Visa Applications
Immigration business plans are critical for securing U.S. visas like the E-2, L-1, and EB-5. These plans must be detailed, compliant with U.S. immigration regulations, and tailored to the specific visa type. Below, we break down the key elements and visa-specific business plan requirements.
Introduction to U.S. Immigration Business Plans
Immigration business plans serve a dual purpose: they present the viability of your business to immigration authorities and demonstrate how your enterprise aligns with U.S. visa requirements.
Tailored Visa Solutions
Customized guidance for choosing the best U.S. immigration visa.
Simplified Process
We streamline your US visa application, reducing complexity and delays.

Expert Assistance
Full support from eligibility checks to application submission.

Proven Success
A trusted track record in securing US visas for various categories.
What is an Immigration Business Plan?
An immigration business plan is a specialized document that outlines your business objectives, strategies, and financial projections to meet the requirements for U.S. visa programs like the E-2, L-1, and EB-5. Unlike traditional business plans, immigration business plans must focus on job creation, investment, and long-term sustainability to align with U.S. immigration laws.
Key Features:
- Financial Projections: Demonstrating the ability to sustain the business and create jobs.
- Job Creation: Showing how the business will contribute to the U.S. economy.
- Detailed Operations Plan: How the business will be run, including staffing and growth plans.
Why Immigration Business Plans are Crucial for Visa Approvals
Immigration business plans are crucial because U.S. immigration authorities use them to assess whether your business:
- Meets the visa requirements, including job creation and economic impact.
- Is viable and sustainable in the long term.
- Provides significant economic benefits to the U.S.
Example: For an E-2 Visa, the business plan must show a substantial investment that is not marginal, meaning it has to generate more than just enough income for the investor and family.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Immigration Business Plans
- Purpose: Traditional business plans focus on guiding business operations and attracting investors, while immigration business plans are designed to meet specific visa requirements and convince immigration authorities of the business’s viability.
- Audience: Traditional plans are typically created for banks, investors, or internal management. Immigration business plans are tailored for U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) or other immigration authorities.
- Focus: Immigration plans emphasize job creation, economic impact, and compliance with visa regulations, whereas traditional plans prioritize profitability and growth projections.
- Detail Level: Immigration business plans require more detailed descriptions of the business model, hiring strategies, and local economic impact, while traditional plans may be more flexible and broad in scope.
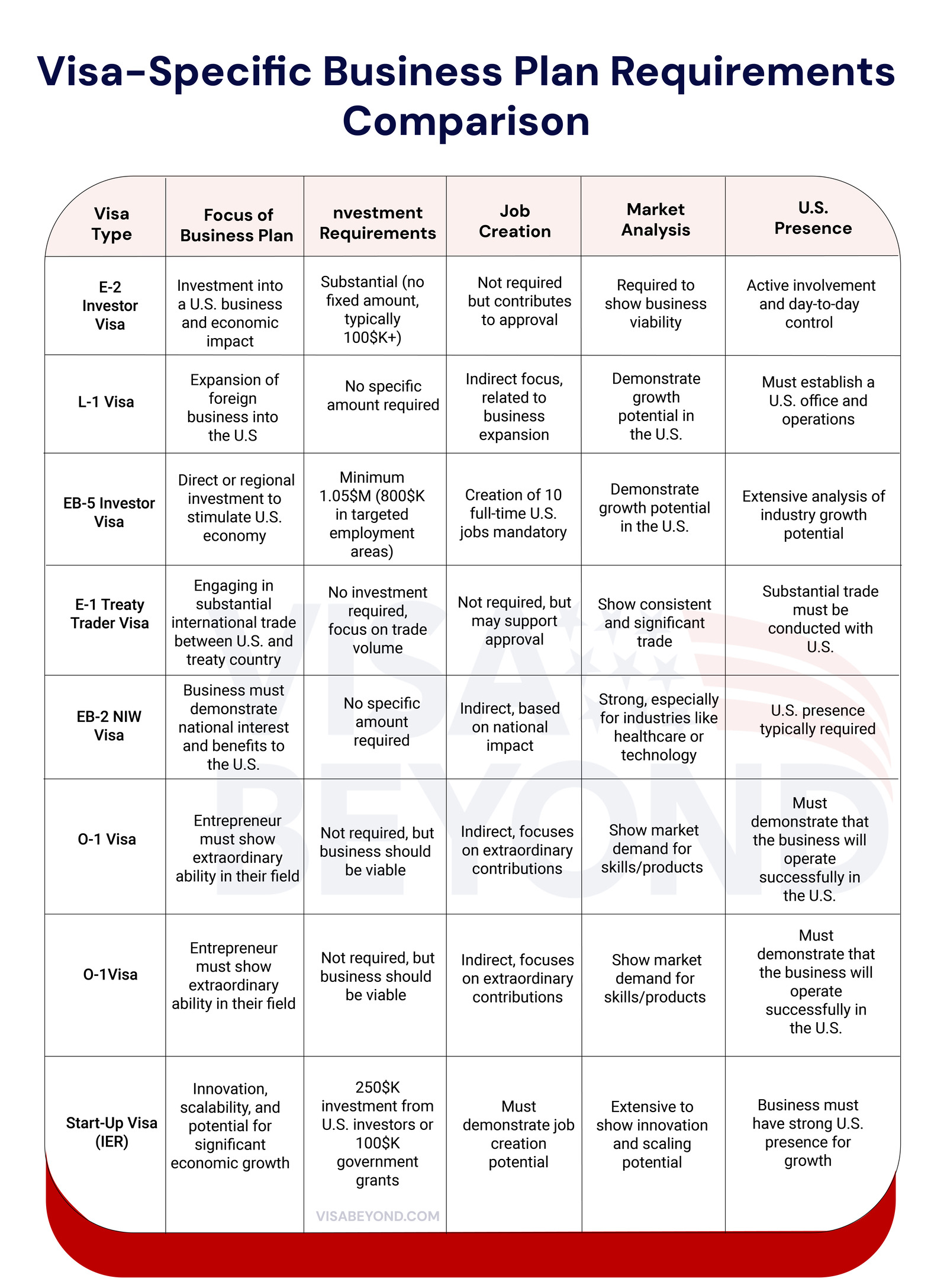
Common U.S. Visas Requiring Business Plans
Several U.S. visas require a business plan as part of the application process. Below are the most common:
- E-2 Visa (Investor Visa): Requires substantial investment and job creation.
- L-1 Visa (Intra-Company Transfer): Must show business expansion into the U.S.
- EB-5 Visa (Immigrant Investor Program): Requires significant capital investment and job creation.
- E-1 Visa (Treaty Trader Visa): Focuses on international trade between the U.S. and the treaty country.
E-2 Visa Business Plan
The E-2 Investor Visa is designed for individuals from treaty countries who make a substantial investment in a U.S. business.
Overview of the E-2 Investor Visa
The E-2 Visa allows foreign investors to enter and work in the U.S. based on their investment in a U.S. business. To qualify, the applicant must:
- Be a national of a country that has a treaty of commerce with the U.S.
- Make a substantial investment in a new or existing U.S. business.
- Play an active role in the business.
Key Requirements for an E-2 Visa Business Plan
To succeed in obtaining an E-2 Visa, your business plan must meet these key requirements:
- Substantial Investment: Show that the investment is sufficient to ensure the business’s success.
- Operational Role: Demonstrate that the investor will actively direct the business.
- Job Creation: Indicate how the business will create U.S. jobs.
Investment Requirements for E-2 Visa Business Plans
The investment must be substantial relative to the total cost of purchasing or establishing the business. There’s no set minimum, but typically investments of at least $100,000 are considered sufficient.
Example: If you’re starting a coffee shop, investing $150,000 for equipment, leases, and employee salaries would likely meet the E-2 investment threshold.
Essential Elements of an E-2 Business Plan
An E-2 business plan should include the following:
- Business Overview: A clear description of the business model.
- Investment Breakdown: A detailed account of how funds will be used.
- Market Research: Showing the business’s potential to succeed in the U.S. market.
- Financial Projections: Typically 5-year forecasts, showing profitability and job creation.
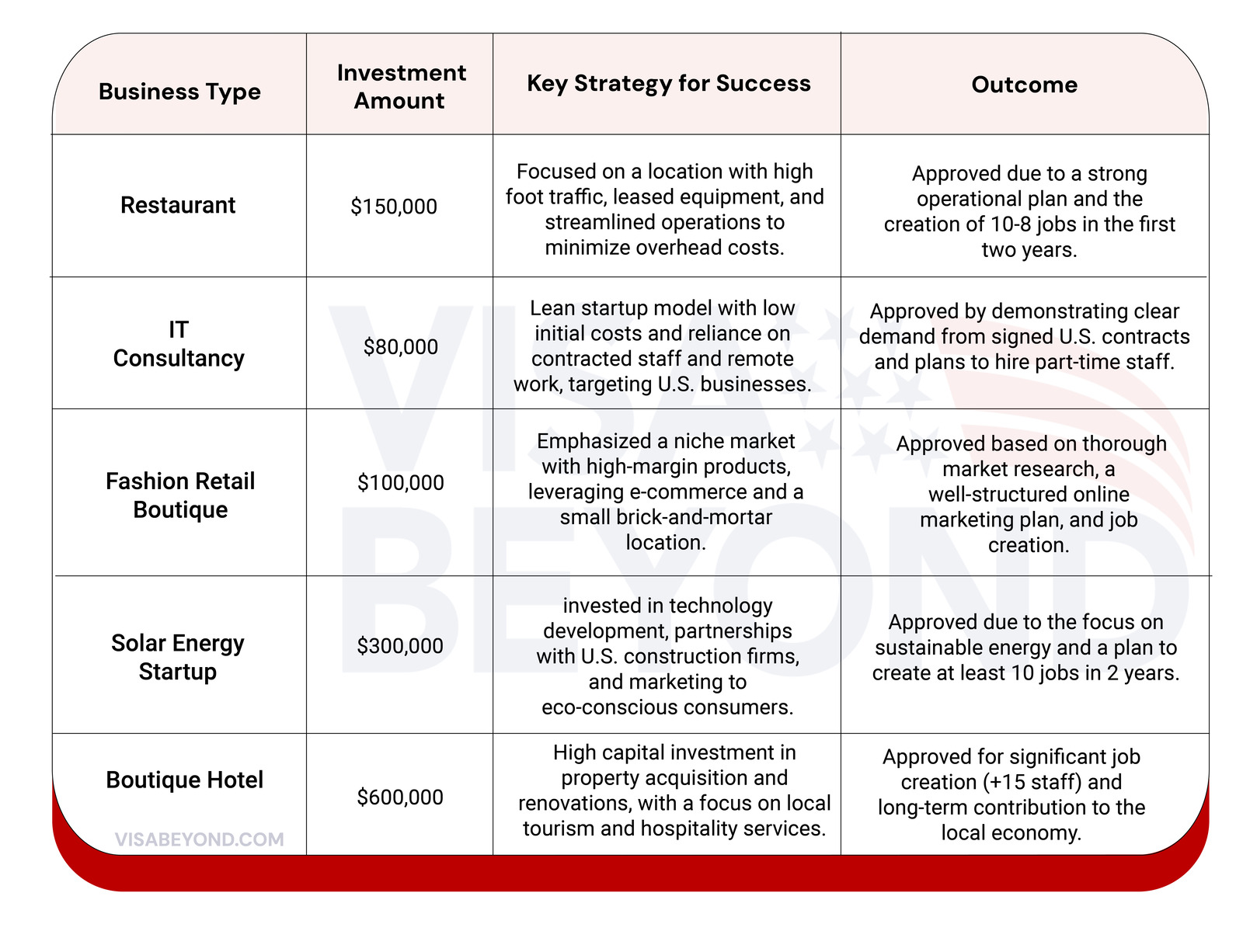
Successful E-2 Business Plan Examples
L-1 Visa Business Plan
The L-1 Visa is for executives or managers who are transferring to a U.S. branch of their foreign company. The business plan must demonstrate how the U.S. entity will grow and contribute to the U.S. economy.
Introduction to the L-1 Visa
The L-1 Visa allows foreign companies to transfer an executive or manager to a U.S. branch. There are two types:
- L-1A: For executives and managers.
- L-1B: For employees with specialized knowledge.
The business plan must show that the U.S. branch is either already operational or will become operational within a year.
L-1A vs. L-1B Visa Business Plan Requirements
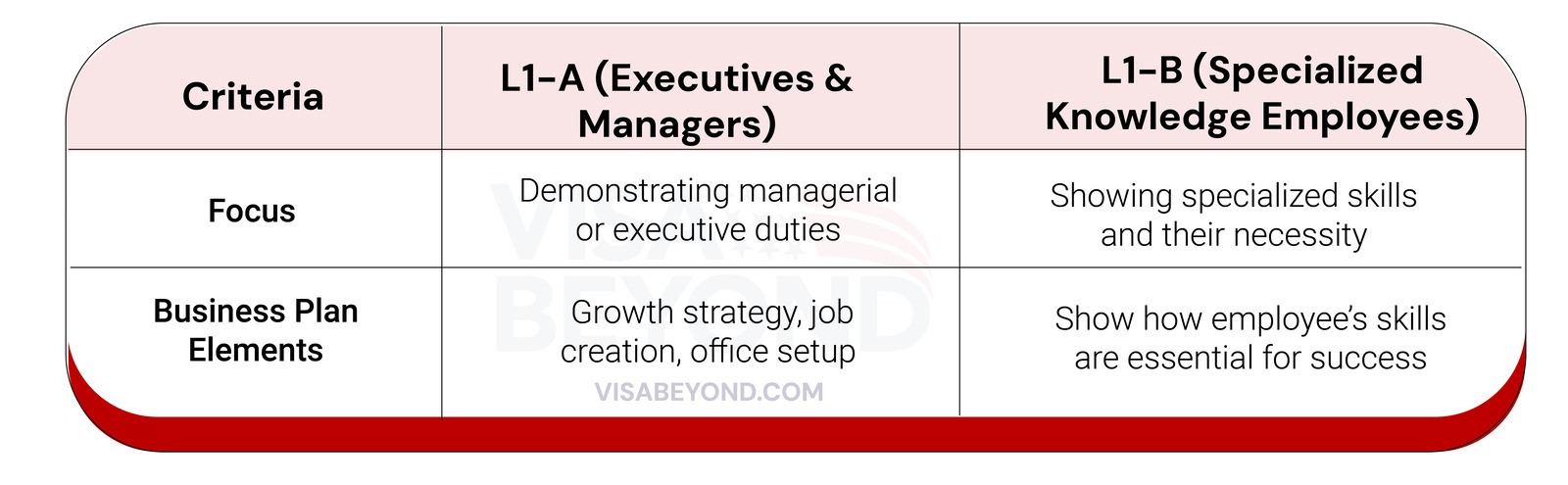
Structure of an L-1 Business Expansion Plan
Your business plan for an L-1 Visa should include:
- U.S. Office Setup: Detail how the U.S. entity will function, including the office space and staffing.
- Organizational Chart: A breakdown of key roles, including the L-1 employee.
- Revenue and Job Growth Projections: A 3-5 year forecast showing the expected growth in revenues and employee count.
U.S. Office Setup in L-1 Visa Business Plans
For L-1 visas, it’s critical to show that the U.S. office will be fully operational. Include details such as:
- Office Lease: Proof of office space or a lease agreement.
- Staffing Plans: How many employees will be hired and their roles.
- Managerial Oversight: How the L-1 applicant will manage operations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in L-1 Visa Business Plans
- Lack of Financial Detail: Incomplete financial projections can cause delays.
- Insufficient Proof of U.S. Operations: Failing to provide evidence of office space or staff plans.
- Overgeneralization: A vague description of the L-1 employee’s role can lead to visa denials.
EB-5 Investor Visa Business Plan
The EB-5 Investor Visa is a direct pathway to U.S. permanent residency for individuals who invest a minimum of $1.05 million (or $800,000 in targeted areas) and create at least 10 full-time U.S. jobs.
Understanding the EB-5 Investor Visa
The EB-5 Visa allows foreign nationals to obtain U.S. green cards by making a qualifying investment in a new or existing business. The business must create at least 10 full-time jobs for U.S. workers.
EB-5 Regional Center Business Plans vs. Direct EB-5 Plans
When applying for the EB-5 Investor Visa, applicants have two primary options: investing through a Regional Center or making a Direct Investment. Each option comes with specific requirements for business plans.
- Investment Type: Regional Center plans involve pooled investments, while Direct EB-5 plans require direct management and investment in a specific business.
- Job Creation: Regional Center plans can count indirect and induced jobs, whereas Direct EB-5 plans must create 10 direct, full-time jobs.
- Involvement Level: Regional Center investments are more passive, while Direct EB-5 investments require active participation in business operations.
- Documentation: Regional Center plans emphasize economic impact studies, while Direct EB-5 plans focus on detailed operational strategies and direct employment plans.
Key Components of an EB-5 Compliant Business Plan
An EB-5 compliant business plan must clearly demonstrate how the business will create jobs and meet the minimum investment threshold. These plans are critical in showing how the business contributes to the U.S. economy.
Components to Include:
- Executive Summary: Brief overview of the business.
- Job Creation Plan: Outline how the business will create at least 10 full-time U.S. jobs.
- Market Analysis: Show demand for your product/service and competitive advantages.
- Financial Projections: Provide 5-year forecasts including profit, revenue, and expenses.
- Investment Structure: Breakdown of how the investment will be used.
Example: A direct EB-5 investment in a renewable energy company must include a detailed job creation plan, financial projections, and a robust market analysis to prove the project’s viability.
Job Creation Requirements in EB-5 Visa Business Plans
The EB-5 program requires the creation of at least 10 full-time U.S. jobs per investor. These jobs can be:
- Direct jobs: Jobs created directly by the business.
- Indirect jobs: Jobs created by the broader economic impact of the business (primarily applicable in Regional Centers).
Key Tip: When creating a business plan, ensure to detail how the business will meet these job creation requirements over a 2-3 year period, and how you will track this growth.
E-1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
The E-1 Visa allows nationals of treaty countries to enter the U.S. to engage in substantial trade, either of goods or services, between their home country and the U.S.
Overview of the E-1 Visa for Treaty Traders
The E-1 Visa is designed for individuals or companies who conduct substantial trade between the U.S. and a treaty country. Unlike the E-2 Investor Visa, the E-1 focuses primarily on the volume of international trade rather than a direct investment into a U.S. business.
Requirements:
- 50% of trade must occur between the U.S. and the treaty country.
- Substantial trade refers to an ongoing flow of goods or services rather than a single transaction.
Trade Requirements for E-1 Visa Business Plans
An E-1 Visa business plan must demonstrate that substantial trade is already taking place or will occur between the U.S. and the applicant’s home country.
Key Points:
- Volume of Trade: Prove a continuous flow of goods or services.
- Industry-Specific Metrics: Highlight contracts, shipping records, or service agreements that demonstrate active trade.
- Sustainability: Show how trade will continue to grow, including future contracts and partnerships.
Demonstrating Substantial Trade in an E-1 Business Plan
To successfully demonstrate substantial trade, your business plan should include:
- Trade Volume: A list of completed and ongoing transactions, including shipping records or invoices.
- Trade Relationships: Describe partnerships and key clients.
- Future Projections: Include contracts that are set to renew or expand in the coming years.
Example: A company that imports machinery parts from Germany to the U.S. might show a steady flow of shipments and existing contracts with multiple U.S. distributors.
Strategic Elements of a Winning E-1 Business Plan
For a successful E-1 visa business plan:
- Emphasize Key Clients: Highlight long-term clients and contracts.
- Focus on Sustainability: Show that your business is built for continued trade growth.
- Track Record: Provide evidence of past success in trade, such as shipping data, contracts, or service agreements.
Pro Tip: Your business plan should show not just current trade but how your business will continue to expand, such as by targeting new markets or increasing volumes with existing clients.
EB-2 National Interest Waiver (NIW) Business Plan
The EB-2 National Interest Waiver (NIW) allows certain individuals to bypass the standard labor certification process by proving that their work is in the national interest of the U.S.
What is the EB-2 NIW Visa?
The EB-2 NIW Visa is a second-preference employment-based visa that waives the standard labor certification process. To qualify, the applicant must demonstrate that their work is of substantial intrinsic merit and will benefit the U.S. on a national scale.
Typical Candidates: Entrepreneurs, researchers, doctors, or individuals in fields like technology and education who can demonstrate their work benefits the national economy, public health, or government interests.
Role of a Business Plan in the NIW Petition
While not always required, a business plan can strongly support an NIW petition if the applicant is an entrepreneur or intends to create a U.S.-based business that provides significant public benefits.
Key Aspects to Include:
- National Impact: Show how your business aligns with national interests (e.g., innovation, job creation, public welfare).
- Economic Benefits: Prove how your business will improve the U.S. economy or employment landscape.
- Innovation: Highlight any groundbreaking work that could provide long-term benefits to the U.S.
How to Show National Interest Through a Business Plan
To demonstrate national interest, focus on the following areas:
- Public Health or Safety: For healthcare businesses or innovations that contribute to national well-being.
- Economic Growth: Outline how your business will create jobs or contribute to key industries like technology, infrastructure, or green energy.
- Technological Advancements: If your business is developing new technology, show how it will give the U.S. a competitive edge globally.
Business Plan vs. Personal Statement for NIW
While the business plan details the specifics of your entrepreneurial endeavors, the personal statement should focus on your professional background and how your skills directly benefit the U.S.
Key Differences:
- Business Plan: Focuses on the business’s long-term viability and its economic or social contributions to the U.S.
- Personal Statement: Emphasizes your qualifications, experience, and why your skills are in the national interest.
O-1 Visa Business Plan
The O-1 Visa is for individuals with extraordinary ability in fields such as arts, sciences, education, business, or athletics. For entrepreneurs, a business plan can help showcase their innovative ideas and contributions to their field.
The O-1 Visa for Individuals with Extraordinary Ability
The O-1 Visa is for individuals who have demonstrated extraordinary ability in their field. Applicants must show sustained national or international acclaim and that they will continue to work in their area of expertise in the U.S.
Common Fields:
- Arts & Entertainment
- Science & Technology
- Business & Entrepreneurship
Why O-1 Visa Applicants May Need a Business Plan
Although the O-1 Visa is primarily focused on proving extraordinary ability, entrepreneurs or self-employed individuals may need to provide a business plan to show how their work will continue to benefit the U.S. economy or contribute to their field.
Reasons for Including a Business Plan:
- Demonstrates Economic Viability: For entrepreneurs, a business plan shows how the venture will generate revenue and provide value.
- Provides Proof of Work Continuity: It highlights how the O-1 applicant’s extraordinary skills will be applied in a business setting.
- Job Creation: A well-drafted business plan shows how the applicant’s business will create jobs and contribute to the U.S. economy.
Business Plan for O-1 Entrepreneurs and Self-Employed
For O-1 entrepreneurs and self-employed individuals, a business plan is a key tool to demonstrate how their extraordinary ability translates into a successful venture in the U.S. The business plan should outline how their expertise, innovation, or creativity will drive the business and contribute to the field or industry.
Focus Areas:
- Unique Skills: Show how the applicant’s exceptional abilities are a driving force behind the business.
- Market Demand: Prove that there is a demand for the applicant’s skills or products in the U.S. market.
- Job Creation and Economic Impact: Highlight how the business will create opportunities for U.S. workers.
Essential Components of an O-1 Visa Business Plan
An O-1 Visa business plan for entrepreneurs and self-employed individuals should include these key components:
- Executive Summary: A clear, concise overview of the business, the applicant’s extraordinary qualifications, and the goals for the U.S. market.
- Description of Products/Services: Detailing how the applicant’s unique abilities contribute to innovative products or services.
- Market Analysis: Show the market demand for the business in the U.S. and how it will meet that demand.
- Operational Plan: How the business will function on a day-to-day basis.
- Financial Projections: Include a 5-year forecast to show the business’s growth potential and how it will contribute to the U.S. economy.
Start-Up Visa and International Entrepreneur Rule Business Plan
The Start-Up Visa path, under the International Entrepreneur Rule (IER), allows international entrepreneurs to build and grow their businesses in the U.S. This visa type requires a strong business plan that showcases the scalability and innovation of the business idea.
Overview of the Start-Up Visa Path
The Start-Up Visa is not a traditional visa category, but a parole program under the International Entrepreneur Rule (IER). It allows foreign entrepreneurs to live and work in the U.S. if they have an innovative business idea that shows significant potential for rapid growth and job creation.
Key Points:
- Entrepreneurs must demonstrate that they have received significant investment from U.S. investors or government grants.
- The business must show the potential for rapid growth and job creation in the U.S.
Key Requirements for a Start-Up Visa Business Plan
A Start-Up Visa business plan must focus on demonstrating the innovation and scalability of the business. Immigration authorities need to see how the business will grow and contribute to the U.S. economy.
Requirements:
- Innovation: The business should be solving a problem or filling a market gap in a unique way.
- Funding: The business must have secured at least $250,000 in U.S. venture capital funding or $100,000 from government grants.
- Scalability: The plan should demonstrate how the business can scale to create jobs and expand in the U.S. market.
Elements of a Compelling Start-Up Business Plan
To create a compelling Start-Up Visa business plan, include the following elements:
- Innovation: Clearly explain the unique product or service and its market potential.
- Market Entry Strategy: How the business plans to penetrate the U.S. market and gain customers.
- Funding Structure: Show where the funding has come from (investors, grants) and how it will be used to grow the business.
- Financial Projections: Include a 5-year financial forecast, showing profitability and growth.
Showing Scalability and Innovation in a Start-Up Business Plan
Scalability and innovation are key for the Start-Up Visa path. To demonstrate these, focus on:
- Growth Potential: Show how the business can rapidly grow, create jobs, and scale its operations in the U.S.
- Disruptive Technology: If applicable, highlight how the business uses technology to disrupt or enhance its industry.
- Investment Strategy: Clearly outline how further investment will be utilized to expand operations and generate jobs.
Let’s Make Your U.S. Dreams a Reality.
What Makes a Strong Immigration Business Plan?
A strong immigration business plan is not just about the business itself; it must also align with the specific visa requirements. It should demonstrate the business’s financial viability, economic impact, and job creation potential in the U.S.
Essential Components of an Immigration Business Plan
An immigration business plan typically includes the following essential components:
Business Overview
The business overview is a concise summary of the company, including its mission, vision, products or services, and key objectives. This section sets the stage for the entire business plan.
Market Analysis and Research
A thorough market analysis shows immigration authorities that your business has researched its target market and understands its competitors, potential customers, and market trends. This section should demonstrate demand for the business's products or services.
Financial Projections and Budget
This section provides detailed financial forecasts (typically 3-5 years) including:
- Projected revenue, expenses, and profitability.
- Break-even analysis.
- Cash flow projections.
Staffing and Job Creation Plans
Job creation is a crucial factor for most visa types. Detail the number of jobs the business will create and what roles need to be filled.
Tip: Include timelines for when new employees will be hired.
U.S. Market Entry Strategy
Outline the strategy for entering and expanding within the U.S. market, including:
- Marketing and sales strategies.
- Distribution channels.
- Key partnerships or networks.
How to Customize Your Business Plan for Visa-Specific Requirements
Customizing the business plan to meet visa-specific requirements is crucial. For instance:
- E-2 Visa: Focus on the investment and how it will contribute to the U.S. economy.
- EB-5 Visa: Emphasize job creation and meeting the investment threshold.
- L-1 Visa: Highlight the connection between the U.S. entity and the foreign company, and how the business will expand.
Common Mistakes in Immigration Business Plans
Avoid these common mistakes in immigration business plans:
- Lack of Financial Detail: Incomplete or vague financial projections.
- Ignoring Visa Requirements: Failing to address specific visa criteria.
- Weak Market Research: Not providing enough evidence to support demand for the business.
Professional Tips for Preparing a Visa-Ready Business Plan
- Hire a Professional: Immigration business plans are complex, and hiring an expert ensures accuracy and compliance.
- Focus on Compliance: Make sure the plan is tailored to the visa requirements.
- Be Detailed but Concise: Include all necessary information without making the plan too lengthy or confusing.
Supporting Documents for Immigration Business Plans
In addition to the business plan, visa applications often require supporting documents that provide additional evidence of the business’s viability.
Key Documents to Include with Your Business Plan
Financial Statements
Provide accurate and up-to-date financial statements, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
Organizational Charts
Include organizational charts showing the structure of the business, key personnel, and their roles.
Proof of Investment or Trade
For investment-related visas, provide proof of funds or trade agreements that substantiate the claims made in the business plan.
Lease Agreements or Contracts
If applicable, include lease agreements, contracts, or other legal documents that demonstrate the business's operations and commitments in the U.S.
How to Build a Supporting Document Package for Your Visa Application
To build a complete and compelling supporting document package for your visa application, follow these steps:
1. Gather Financial and Legal Documents:
Include all documents mentioned in the business plan, such as financial statements, tax returns, proof of investment, contracts, and trade agreements. Ensure they are up to date and accurate.
2. Organize Logically:
Create a table of contents for your supporting documents and organize them in a logical order that aligns with your business plan. For instance, group financial documents together, followed by legal agreements, proof of investment, and contracts.
3. Label Each Document Clearly:
Clearly label each document in your package. Immigration officials may review dozens of pages, so clear labeling helps them find the information they need efficiently. Include brief explanations if necessary.
4. Provide Certification for Translations:
If any of your documents are in a language other than English, provide certified translations. This ensures that immigration officers can easily understand the content without delay.
5. Consult Experts:
Work with an immigration attorney or business consultant to review your document package for completeness and accuracy. Missing or poorly organized documents can delay the approval process.
FAQs About U.S. Immigration Visa Plans
What is a U.S. immigration visa?
A U.S. immigration visa is a document that allows foreign nationals to enter the U.S. for permanent residency. There are various categories, such as family-based, employment-based, and investment visas, each with its own specific requirements.
What are the requirements to apply for a U.S. work visa?
To apply for a US work visa, you generally need a job offer from a U.S. employer who will sponsor your visa, along with demonstrating your qualifications and ensuring the job meets specific visa requirements.
How long does the U.S. work visa process take?
The timeline for obtaining a US work visa can vary depending on the visa type, country of origin, and processing times at U.S. consulates or immigration offices. It can take anywhere from a few months to over a year.
Can I apply for permanent residency through a work visa?
Yes, many U.S. work visas, such as the H-1B or EB categories, can be pathways to permanent residency (green card), depending on your qualifications, employer sponsorship, and adherence to immigration laws.
What is the difference between a U.S. immigration visa and a non-immigrant visa?
A U.S. immigration visa is for individuals seeking permanent residency, while a non-immigrant visa allows for temporary stay, such as for tourism, business, or short-term work.
Do U.S. work visas have a quota or limit?
Some US work visas, like the H-1B, have annual quotas, meaning only a certain number of visas are issued each year. Other visas, such as the L-1, do not have such caps.
Can I change employers while on a U.S. work visa?
In some cases, it is possible to change employers while on a US work visa, but you typically need to go through a transfer process, and your new employer must also sponsor your visa.
Visa Guidance
We provide personalized advice on selecting the right U.S. immigration visa based on your specific goals, whether it’s for employment, investment, or family-based immigration, ensuring that you meet all the necessary requirements for a successful application.
Documentation Support
Our team assists with preparing and organizing all necessary documents, including visa applications, sponsorship letters, and supporting evidence, to ensure a smooth and efficient process while avoiding common errors or delays.
Legal Assistance
We offer continuous legal support throughout the entire immigration process, including responding to requests for additional information, handling any visa-related issues, and advising on pathways to permanent residency or citizenship once you’re in the U.S.








We help to achieve
mutual goals.
Latest News.
From the blog

-
- Posted by Alvez

-
- Posted by Alvez

-
- Posted by Alvez
"*" indicates required fields

